Quick Start Guide
Getting Meshery up and running locally on a Docker-enabled system or in Kubernetes is easy. Meshery deploys as a set of Docker containers, which can be deployed to either a Docker host or Kubernetes cluster.
Quick Start Assumptions
This quick start guide enables you to download, install, and run Meshery in a single command. See all supported platforms for more specific (and less presumptuous) instructions.1. Download, install, and run Meshery
If you are on a macOS or Linux system, you can download, install, and run both mesheryctl and Meshery Server by executing the following command.
$ curl -L https://meshery.io/install | PLATFORM=kubernetes bash -
Meshery CLI
Meshery's command line interface,mesheryctl, can be installed in various ways. In addition to Bash, you can also use Brew or Scoop to install mesheryctl. Alternatively, mesheryctl is also available via direct download.
2. Access Meshery
Your default browser will be opened and directed to Meshery’s web-based user interface typically found at http://localhost:9081.
Accessing Meshery Server with Meshery UI
Meshery's web-based user interface is embedded in Meshery Server and is available as soon as Meshery starts. The location and port that Meshery UI is exposed varies depending upon your mode of deployment. See accessing Meshery UI for deployment-specific details.Accessing Meshery Server with Meshery CLI
Meshery's command line interface is a client of Meshery Server's REST API (just as Meshery UI is). Choose to usemesheryctl as an alternative client as it suits your needs.
3. Select a Provider
Select from the list of Providers in order to log in to Meshery. Authenticate with your chosen Provider.
4. Configure Connections to your Kubernetes Clusters
Out-of-Cluster Deployments
If you have deployed Meshery out-of-cluster, Meshery Server will automatically attempt to connect to any available Kubernetes clusters found in your kubeconfig (under $HOME/.kube/config) and in kubeconfigs uploaded through Meshery UI. Meshery Server deploys Meshery Operator, MeshSync, and Broker into the meshery namespace (by default).
In-Cluster Deployments If you have deployed Meshery in-cluster, Meshery Server will automatically connect to the Kubernetes API Server available in the control plane.
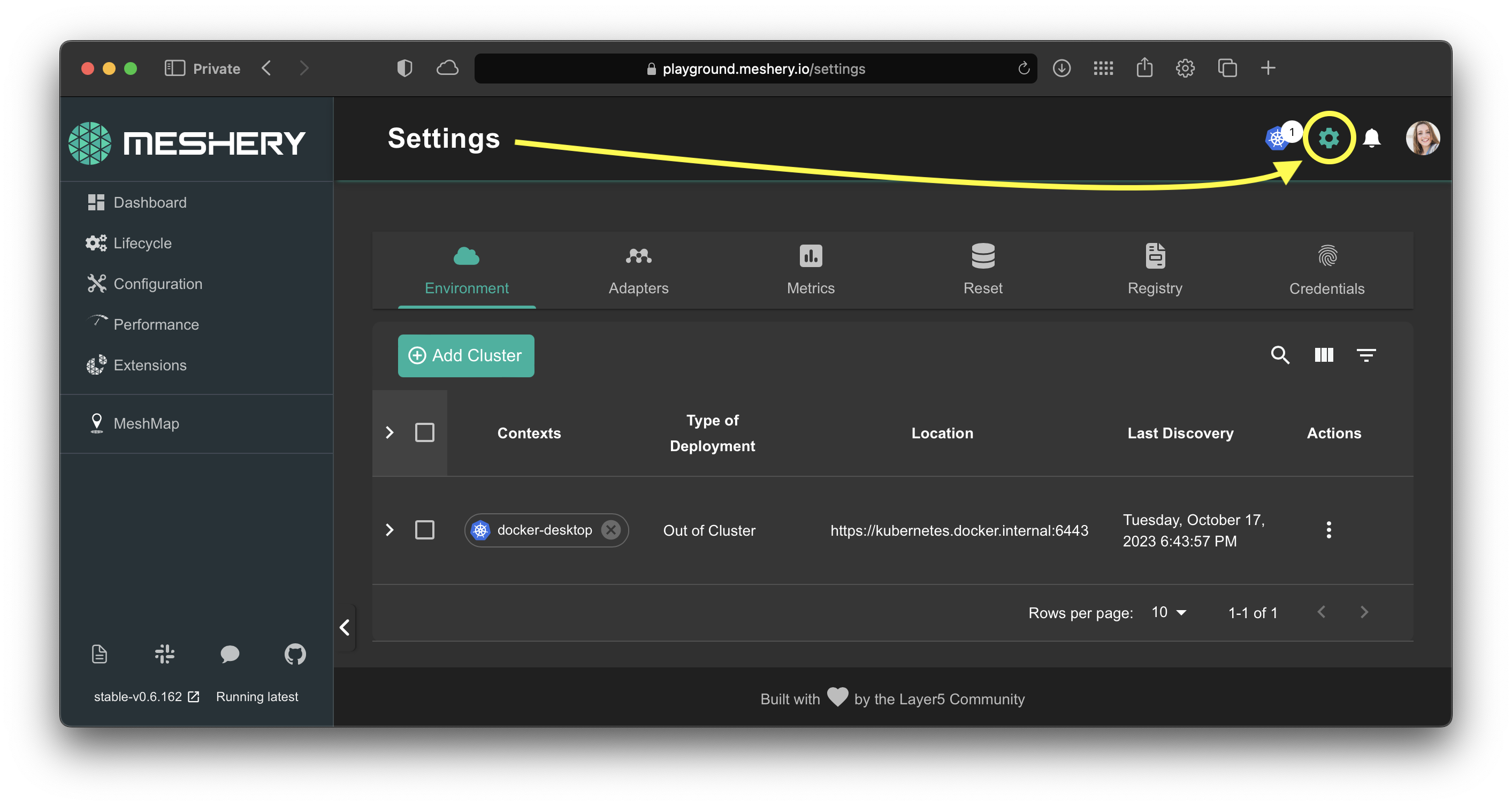
Visit Settings:
If your config has not been autodetected, you can manually upload your kubeconfig file (or any number of kubeconfig files). By default, Meshery will attempt to connect to and deploy Meshery Operator to each reachable context contained in the imported kubeconfig files. See Managing Kubernetes Clusters for more information.
5. Verify Deployment
Run connectivity tests and verify the health of your Meshery system. Verify Meshery’s connection to your Kubernetes clusters by clicking on the connection chip. A quick connectivity test will run and inform you of Meshery’s ability to reach and authenticate to your Kubernetes control plane(s). You will be notified of your connection status. You can also verify any other connection between Meshery and either its components (like Meshery Adapters) or other managed infrastructure by clicking on any of the connection chips. When clicked, a chip will perform an ad hoc connectivity test.
6. Design and operate Kubernetes clusters and their workloads
You may now proceed to manage any cloud native infrastructure supported by Meshery. See all integrations for a complete list of supported infrastructure.
Explore Tutorials
🧑🔬 Explore these tutorials to learn how to use Meshery for collaboratively managing infrastructure.
- Deploying Apache Cassandra with a StatefulSet in Meshery Playground
- Deploying PHP Guestbook application with Redis in Meshery
- Exploring Kubernetes CronJobs
- Exploring Kubernetes Services with Meshery
- Understanding Kubernetes ConfigMaps and Secrets with Meshery
- Exploring Kubernetes Deployments with Meshery
- Exploring Kubernetes Pods with Meshery
- Kubernetes Request Flow – A Visual Guide
- Deploying WordPress and MySQL with Persistent Volumes with Meshery